Originally published July 30, 2019 , updated on September 9, 2024
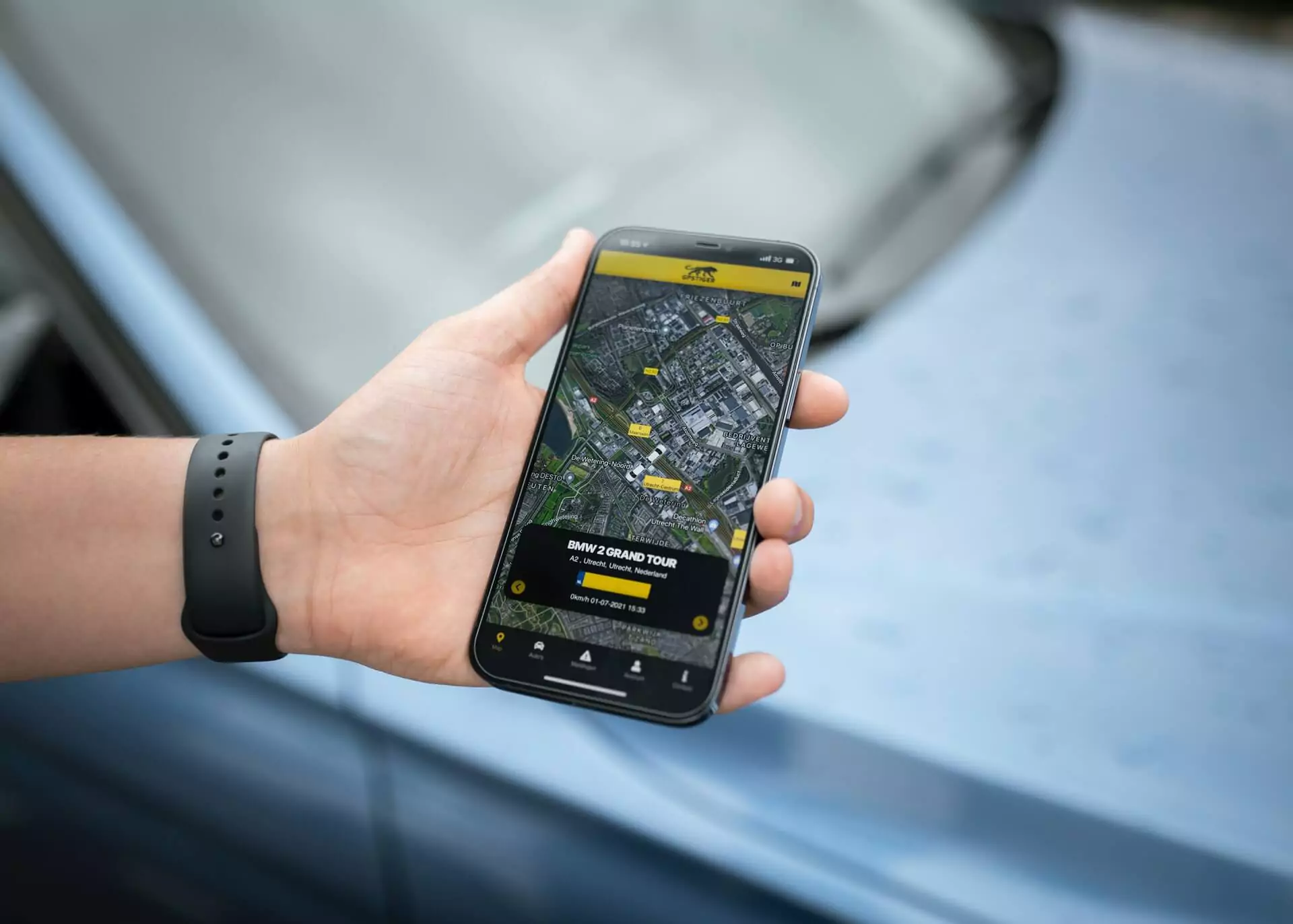
The term ‘geo-location app’ refers to a type of app that shows someone your location. Alternatively, it shows where you are in relation to other landmarks. Examples would be:
-
Uber, which shows a driver where to come and fetch you as well as where to drop you off, and
-
Google Maps, which allows you the ability to see where you are and will help you navigate to where you want to go.
In order for this app to work, the user has to have their phone’s GPS enabled. These apps obviously don’t tell just anyone where they are – if they want to be found, they will enable the app to show your location.
How to Build Geo-location Apps That Work For You

Before even thinking about building your own geo-location app – or hiring a team of developers to build it for you – you need to spend some time on the planning process.
Choose Your Tech Stack
Step one is to choose the technology that you are going to use in order to build the app. In tech speak, this is called a ‘tech stack’. Within your tech stack, you’ll need to choose which ‘APIs’ you are going to use in order to build your app. (Think about an API as a block of Lego. These blocks come in pre-determined shapes and sizes, however you can create new structures with them. The same concept applies to APIs.)
Use the Google Maps API, as well as the Core Location API, to locate at IoS device. To show the location on a map, you can use the Google Maps SDK or Apple MapKit.
To build an Android version of the geo-location app, use Google Location Services API. This permits you to:
-
Determine the position of the with GPS, Wi-Fi, Cell ID, or A-GPS.
-
Discover how the user is moving and react to these changes with notifications or other actions.
-
Determine the distance to selected places such as stores or cafes which can be used to set up geo-fences.
To show a place on a map, it is possible to use:
-
Google Maps API and MapView class,
- The API of
Google Maps Directions, and/or
-
Google Distance Matrix.
It’s also possible to build geo-location apps that use a web interface. Crucial technology in the tech stack that you will choose for this purpose include:
-
W3C Geolocation API, which is supported by most browsers
-
HTML5 geolocation API, and
-
Google Maps API or MapKit JS from Apple.
What to Watch Out for When Building Geo-location Apps
Geo-location apps have the potential to be the basis of incredibly successful businesses and to improve the lives of many of the users of smart devices and the Internet. However, there’s one main reasons why people don’t engage with these types of apps – and may even uninstall them.
Not Respecting Privacy
Geo-location apps contain a lot of personal information, for example, where a person works, where they live and/or their banking details. This means that should a clever hacker successfully gain access to the app’s database, they could wreak untold havoc.

This means that in order to have your geo-location app be successful, you need to safeguard your users’ information extremely carefully. Make sure that you adhere to the privacy laws of your particular country so that – should a data breach happen, for some reason – you won’t be held liable in a court of law and be forced to pay damages or – worse still – face jail time.
Everyone seems to be jumping onto the bandwagon of geo-location apps. As we’ve said previously, they are a great idea for a start of a business or an amazing add-on to increase a business’ value-add to their customers. However, in order to be successful, geo-location apps need to be built correctly.
Post Views: 1261


















